Welcome to the wonderful world of barnacles…
Wait–before you stop reading–did you know that:
- Barnacles are related to lobsters
- Barnacles nearly drove Charles Darwin crazy while he was researching The Origin of the Species
- Barnacles have no heart
- Barnacles have the largest relative penis size in the natural world
All true.
Sailors throughout history have despised the lowly barnacle. They grow quickly on the bottom of a boat, causing hydrodynamic drag that can bring even racing sailboats to a near standstill. Several singlehanded sailors in the most recent Golden Globe race around the world had to dive overboard in the chilly Southern Ocean to remove masses of gooseneck barnacles. Racer Jeremy Bagshaw’s boat, Olleanna, could barely move because of an infestation of barnacles. He said, “I didn’t have enough food to go around the world at three knots.” He could have eaten the gooseneck barnacles. They are considered a delicacy in many parts of the world and sell for as much as $100 a pound. One reviewer said they taste like “eating the sea.” Jeremy Bagshaw didn’t want to eat the sea. He just wanted to sail home.
Barnacles have existed for at least 325 million years, which has a lot to do with the fact that they are really good at making baby barnacles. Described as, among other things, the “genitalia of the sea,” barnacles have had to evolve creatively to survive. They are sessile, meaning they are permanently attached to one place and cannot leave their shells to mate. Some barnacles evolved as hermaphrodites. Another way they facilitate genetic transfer between isolated individuals is with extraordinarily long penises. “Barnacles probably have the largest penis-to-body size ratio of the animal kingdom,” according to a report in New Scientist Magazine. “On exposed shores,” the report continues, “it’s better for barnacles to grow shorter, thicker penises” so that the sexual organ is not damaged in rough sea conditions. Regardless of diameter, the penis of a barnacle only lasts for one mating season, and it is then discarded. Fortunately, it will grow a new one the following year.
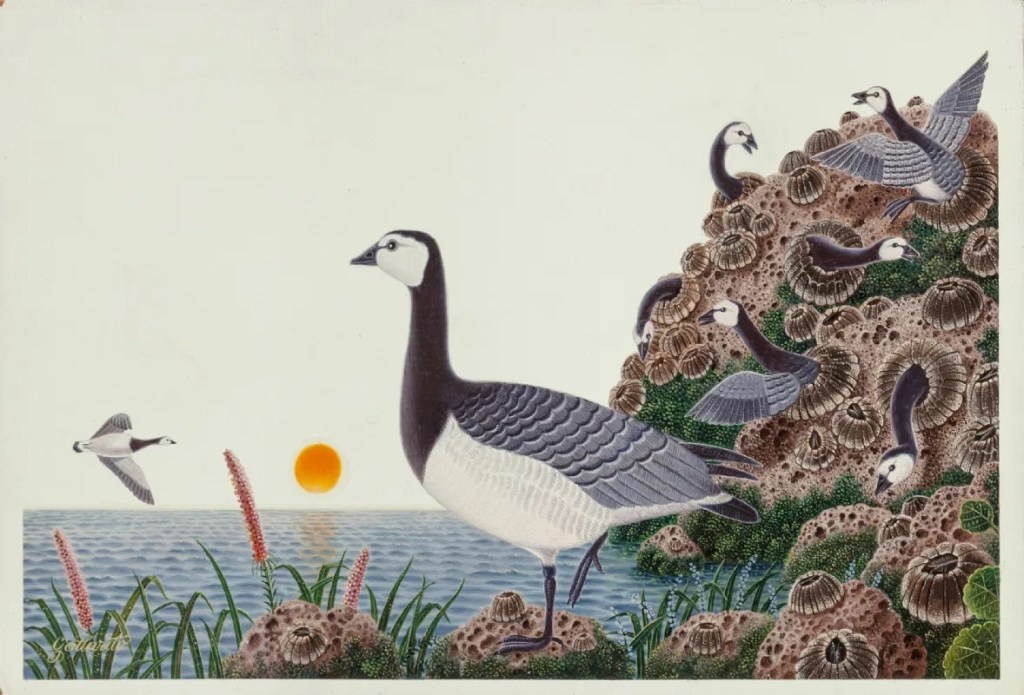
While the science of a barnacle’s sex life is strange, the medieval bestiary folklore about these creatures is downright bizarre. The 12th-century religious historian, Gerald of Wales, proclaimed that geese (yes, birds) hatched from barnacles attached to driftwood. He wrote: “They hang down by their beaks as if they were a seaweed attached to the timber. I have frequently seen, with my own eyes, more than a thousand of these small bodies of birds, hanging down on the sea-shore from one piece of timber, enclosed in their shells, and already formed.” For some reason, there is a statue honoring Gerald of Wales in Britain’s St Davids Cathedral.
In the 1600s, another disreputable English author and illustrator, John Gerard, perpetuated the myth by claiming to have seen geese emerging from the shells of barnacles. The legend persisted through the 1800s, when, even while the Industrial Revolution was occurring in Britain, some people apparently still believed that live birds emerged from the shells of marine invertebrates.
Famed naturalists Carl Linnaeus and Georges Cuvier were more rational in their observations, but they were convinced that barnacles were mollusks. In 1830, a lesser-known naturalist named William Thompson proved them wrong, and, in a radical reinterpretation of taxonomy, barnacles were reclassified as crustaceans.
Still another Englishman of letters—Charles Darwin, no less—became inspired by barnacles. Inspiration turned into obsession, and Darwin spent eight years trying to understand them. Darwin often worked through the night beneath an oil lamp, dissecting barnacles under the microscope in a room thick with the vapors of preserving spirits. He suffered migraines and intestinal distress, even nightmares. Doctors begged him to stop. Darwin refused. He had begun seeing variations in barnacles no one had ever noticed. His work resulted in a 4-volume monograph on barnacles, living and extinct, and it helped him refine his theory of evolution by natural selection.
Afterward, when asked by an old friend about his passion for barnacles, Darwin responded, “I hate a Barnacle as no man ever did before, not even a Sailor in a slow-sailing ship.”

As always, sailing is not just about the wind and the sea; the places, the flora, fauna, and people encountered along the way are equally important.
Please click “Follow” so you don’t miss a new update, and please consider sharing this post with others who might enjoy connecting with the voyage. I welcome your comments and will always respond when I have an Internet connection. I will never share your personal information.
An additional website, www.JeffreyCardenas.com, features hundreds of fine art images—underwater, maritime landscapes, boats, and mid-ocean sailing photography–from exotic locations worldwide.
Upcoming Exhibition: “On the Reef” will be exhibited in The Studios of Key West’s Zabar Project Gallery, on view from January 2–30, 2025.
Instagram: StellaMarisSailing / Facebook: Jeffrey Cardenas
Text, Photography, and Videos © Jeffrey Cardenas 2024
Let this be a time of grace and peace in our lives – Rev. John C. Baker